On May 9, 2012, the Gates Foundation announced the Grand Challenges Explorations Round 8 winners. More than 100 researchers were awarded $100,000 grants for innovative, early-stage research projects focusing on one of five categories. Some of the winners are featured here.

Arun Ramanujapuram of Logistimo, Inc. in India is developing a “bulletin-board” for mobile phones that can provide real-time availability and demand assessment for vaccines and medicines so that supplies can be redistributed to areas of need and waste reduced.

Michael DuBow of Université Paris-Sud in France is developing a business card impregnated with bacteriophages that target bacterial pathogens. The cards will include illustrated instructions and can be dissolved in a small amount of water and applied to contaminated soil, seeds, and plants.
Eric Henderson of Iowa State University in the U.S. is building an inexpensive nanodevice that uses DNA to interact with biomarkers of target pathogens. When a reaction occurs, a reader in the device will create a visual display indicating the presence of the pathogen.
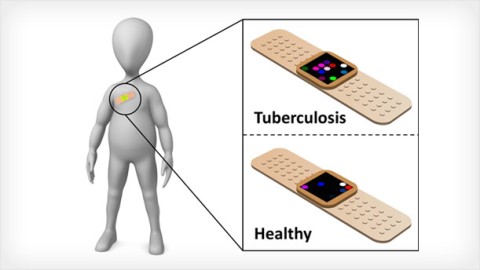
Hossam Haick of Technion - Israel Institute of Technology in Israel is testing a self-administered adhesive sensor that can be placed on the chest to detect biomarkers emitted through the skin that indicate tuberculosis infection.

George Barbastathis and collaborators at the Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology in the U.S. are developing unmanned aerial vehicles that can be deployed by health care workers via cell phones to swiftly deliver vaccines to hard-to-reach locations.
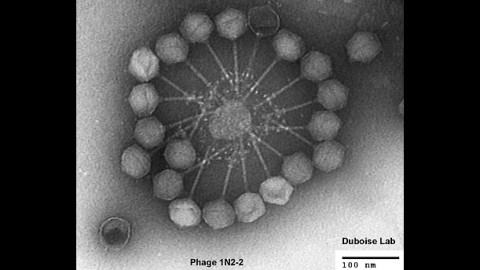
Samuel M. Duboise of the University of Southern Maine in the U.S., along with colleagues in Kenya, is developing a vaccine platform that uses bacteria capable of surviving in extreme environments to produce inexpensive, stable, and easy-to-manufacture vaccines.

Meshack Obonyo of Egerton University Njoro in Kenya is testing a simple solar-powered grain drying unit for its ability to prevent contamination by aflatoxin, a toxic fungal compound.
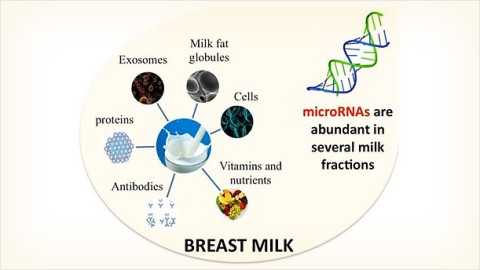
Bogdan Mateescu of ETH University in Switzerland will explore the role of microRNAs that are transmitted from mothers to infants through breast milk and that could be the basis for new supplements to promote healthy infant growth.

Nancy Muller of PATH in the U.S. is developing and field testing a new liner for vaccine carriers to protect vaccines from freezing.
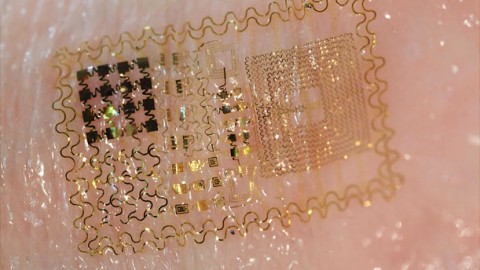
Todd Coleman of the University of California, San Diego in the U.S. is collaborating with John Rogers of the University of Illinois to create wireless tattoo-like electronics that can be placed on the skin to continuously monitor vital signs in pregnant mothers and their unborn babies.

David Hughes of the Pennsylvania State University in the U.S. is working to produce plants that express RNA interference that sterilizes ant queens when ingested. By reducing the number of ants that protect aphids, the aphid population will also drop, reducing damage to important plant crops.

David Segal of the University of California, Davis in the U.S. is developing a high-throughput screen to search for artificial transcription factors that could be used to treat malaria infections.

Maruthi M. N. Gowda of the Natural Resources Institute in the United Kingdom is working to control the population of the whitefly, which transmits plant viruses, by using Wolbachia bacteria that naturally spread through whitefly populations and inhibit the insect’s reproduction and egg laying capabilities.

Laura Woollett of the University of Cincinnati in the U.S. is collaborating with the MRC International Nutrition Group in The Gambia to investigate whether low cholesterol levels in pregnant mothers play a role in low birth weights of infants in poor populations.